| Polarised light |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Photoelasticity in plastic
Plastic sandwiched between crossed Polaroid filters |
Photoelasticity in plastic
Plastic sandwiched between crossed Polaroid filters |
View through car windscreen without Polaroid sun glasses. |
View through car windscreen with Polaroid sun glasses. |
| Rainbows |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Rainbow |
Rainbow |
Rainbow |
|
| The Eye |
 |
|
|
|
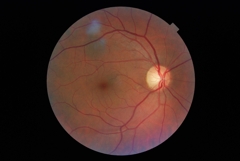
| Fundus camera picture of left eye |
|
|
|
| Diffraction of light |
 |
 |
 |
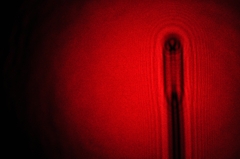 |
| Dispersed laser beam diffracted by a razor blade |
Dispersed laser beam diffracted by a razor blade |
Dispersed laser beam diffracted by a razor blade |
Dispersed laser beam diffracted by a the eye of a needle |
| | | | |
 |
 |
|
|
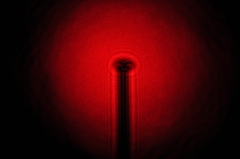
| Dispersed laser beam diffract by a pin head |
Dispersed laser beam diffracted
by open scissors |
|
|
| Interference of light |
 |
|
|
|
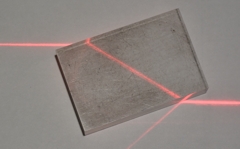
Laser beam on double slit with separation
of 0.27mm
Slit to screen = 7.5m
Distance for 10 fringe spacing =0.175m |
|
|
|
| Spectra |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Spectrum from a glass prism |
Spectrum from a 300 lines/mm grating.
Note it is the opposite way round to the prism spectrum. |
Candle seen through diffraction gratings.
The top is 100lines/mm and the bottom is 300lines/mm |
A white LED viewed through diffraction glasses |
| Refraction |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Spoon in a glass of water |
Pen in a glass of water |
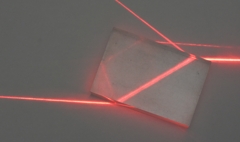
Refraction through a perspex block.
The light enters on the left and emerges parallel on the right.
Light is also reflected as it enters the block |
As the angle of incidence becomes greater, the brightness of the reflected light also increases.
Light is also relfected internally within the block |
| | | | |
 |
 |
 |
|
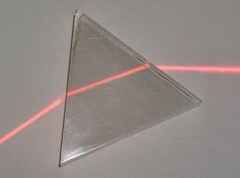
Refraction through a 60° prism.
Light enters from the left |
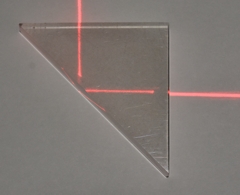
Total internal reflection in a 90° prism.
Light enters from the left |
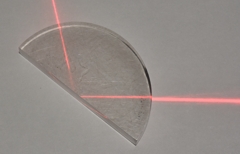
Total internal reflection in a semi-circular perspex block.
Light enters from the left |
|
| Converging Lenses |
 |
 |
 |
|
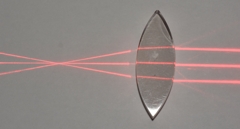
Thick biconvex lens
Rays cross at the focus
Light enters from the left |
Thin biconvex lens
Rays cross at the focus
Light enters from the left |
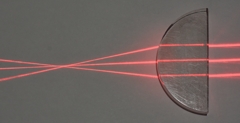
Thick plano-convex lens
Rays cross at the focus
Light enters from the left |
|
| Diverging Lenses |
 |
 |
 |
|
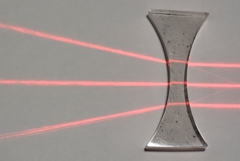
Thick biconcave lens
Rays appear to cross at a focus behind the lens
Light enters from the left |
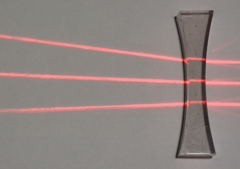
Thin biconcave lens
Rays appear to cross at a focus behind the lens
Light enters from the left |
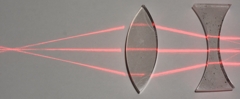
The focal length of the converging lens is increased by the diverging lens
Light enters from the left |
|
| Mirrors |
 |
 |
|
|
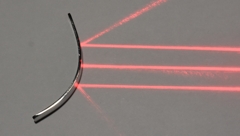
Convex mirror - diverging
Rays appear to cross at a focus behind the mirror
Light enters from the left |
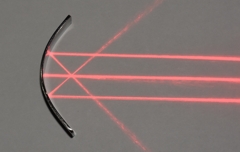
Concave mirror - converging
Rays cross at the focus infront of the mirror
Light enters from the left/td>
| |
|
| Old cameras |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Agfa bellows camera ~1940s |
Coronet Ambassador ~1930 |
Box camera ~1920s |
Kodak Brownie 127 ~1960 |
| Miscellaneous |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Peacock feather |
Caustic curve in a saucepan full of sugar |
Electron diffraction through graphite |
|
| | | | |

