Thermistors

There are two classes of thermistor;
• thermistors whose resistance decreases as the temperature increases (negative temperature coefficient, ntc),
• thermistors whose resistance increases as the temperature increases (positive temperature coefficient, ptc),
ntc thermistors are usually made from a semiconductor material,
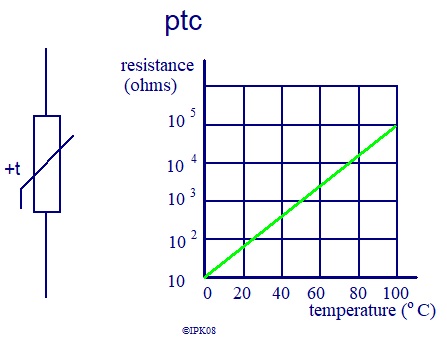
ptc thermistors are usually made from metal materials.
A thermistor can therefore convert changes in temperature into changes in electric current.
The component symbol and a typical characteristic are shown below.
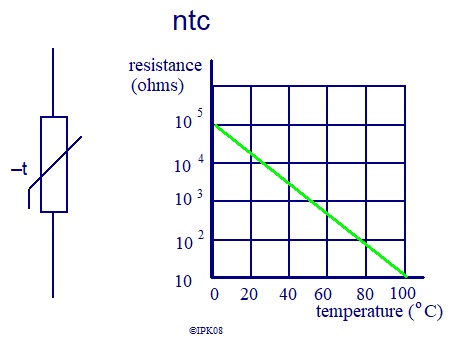
For ntc types, As temperature increases, their resistance decreases.
For ptc types, As temperature increases, their resistance increases.
There are many different types of thermistor available varying in both physical size and the change of resistance with temperature.
Physically smaller thermistors have a faster response time than larger types.
ntc thermistors qare much more common than ptc thermistors.
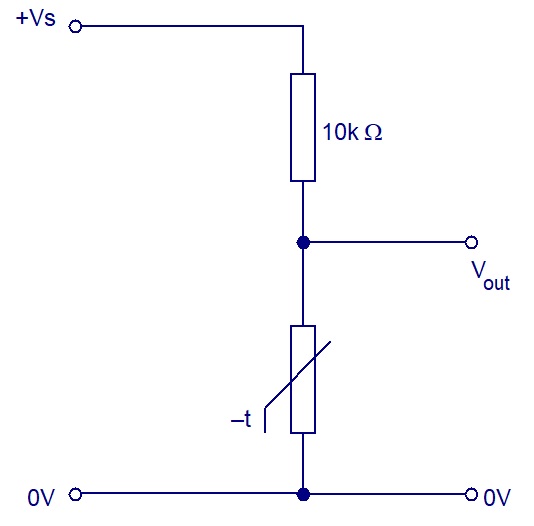
Thermistors have to be used as one of the resistors in a voltage (potential) divider to produce a voltage that changes with temperature.
In the circuit opposite, when the ntc thermistor is hot, its resistance is low and therefore
Vout will be near to the power supply voltage, Vs.
When the ntc thermistor is cold, its resistance is high and therefore Vout will be near to 0V.
(The opposite would be true for a ptc thermistor.)
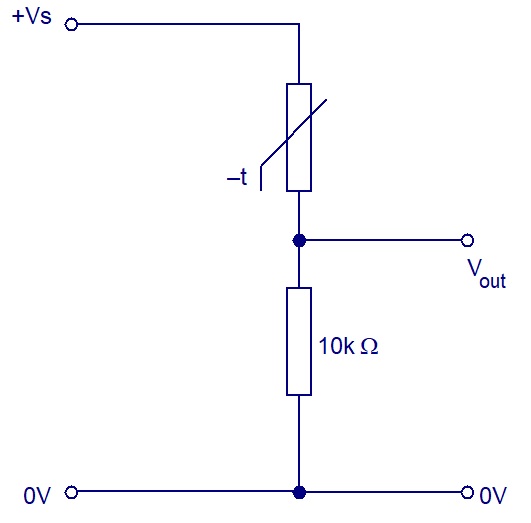
In the circuit opposite, when the ntc thermistor is hot, its resistance is low and therefore Vout will be near to 0V.
When the ntc thermistor is in hot, its resistance is low and therefore Vout will be near to +Vs.
(The opposite would be true for a ptc thermistor.)