
Light Dependent Resistor LDR

The resistance of a light dependent resistor decreases as the illumination on it increases.
It can therefore convert changes in light intensity into changes in electric current.
Its component outline, symbol and a typical characteristic are shown below.
Note: The scales of the axes of the graph for both the illumination and the resistance are logarithmic.

As light level increases, the LDR resistance decreases.
The ORP12 is one readily available LDR.
This type has a response to colour similar to the human eye.
LDRs have a very large change in resistance, but their response time is slow.
LDRs have to be used as one of the resistors in a voltage (potential) divider to produce a voltage that changes with light intensity.
In the circuit opposite, when the LDR is in bright light, its resistance is low and therefore
Vout will be near to the power supply voltage, Vs.
When the LDR is in dark, its resistance is high and therefore Vout will be near to 0V.
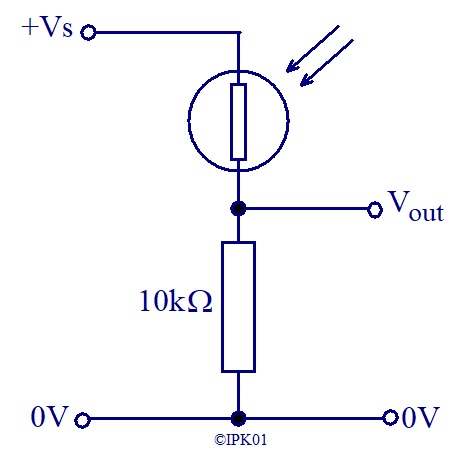
In the circuit opposite, when the LDR is in bright light, its resistance is low and therefore Vout will be near to 0V.
When the LDR is in bright light, its resistance is low and therefore Vout will be near to +Vs.
