
Electricity Fundamentals
Charge is measured in COULOMBS. (C) and is usually given the symbol Q (or q). (Quantity of electricity)
Charge is quantised - the electron carries a quantum of charge = 1.602176634×10-19 C. (Definition)
For historical reasons, the charge on an electron is negative.
All of electricity can be explained in terms of the behaviour of electrons.
It is useful to have a mental image of an electron. This can be anything you like.

When electrons move, an electric current is produced which is measured in AMPs by an AMMETER.
Electric current is given the symbol I (Intensité du courant).
Electric current can be thought of as the number of electrons per second moving past a point.
Electric current is defined as the charge moved divided by the time taken (in seconds).
=> So 1 Amp = 1 Coulomb per second
Current passes THROUGH a circuit.
To measure a current an ammeter has to be connected in SERIES
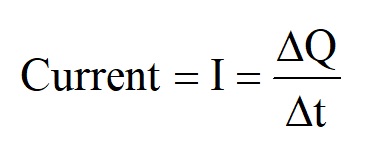
(Definition)
Electrons will only move when they can lose (or gain) energy.
Therefore electrons can only move when there is an energy difference to where they are moving.
I.E, there is a POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE (PD) in their energy.
PD is measured in VOLTS and is often called VOLTAGE.
It is given the symbol V.
PD is measured by a VOLTMETER and is connected ACROSS the circuit so as to measure the energy each electron has.
It has to be connected in PARALLEL.
PD is defined as the energy change per unit charge.
=> So 1 Volt = 1 Joule per Coulomb
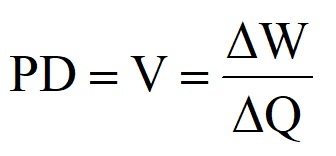
(Definition)
All of the electrons that start to flow around a circuit from a battery end up entering the other side of the battery.
Charge is always conserved.
(This is sometimes called Kirchhoff's first Law)
Electrons do lose (gain) energy by the work that they do in going through the various parts of the circuit.
The total energy lost cannot be greater than the energy they start with.
Energy is always conserved.
(This is sometimes called Kirchhoff's second law.)
Any part of the circuit that causes electrons to lose energy is said to have RESISTANCE.