
The Decibel
Background.
The Bel is a relative unit of power measurement.It is named after Alexander Graham Bell who is usually considered to be the inventor of the telephone.
In his early work on telephones and acoustics, it became apparent that a perceived doubling in sound intensity corresponded to an approximate 10 times increase in power.
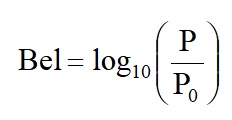
where P is the power and P0 is the reference power.
In practice, this was considered to be too large a unit and so the Decibel, dB, was adopted as the power ratio unit.
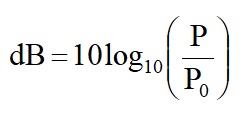 ,
,
E.g. If the reference power is 1W and a radio transmitter has a power output of 100W,
then the radio transmitter has a power output of 10log(100/1) = 20dB relative to the reference power.
If the radio transmitter had only a power output of 1mW, then compared to the reference power, the output would be 10log(0.001/1) = -30dB.
The use of power ratios is very useful when evaluating the overall power amplification of e.g. a radio system,
since the power gain of the whole system is equal to the power gain of each subsystem.
E.g.
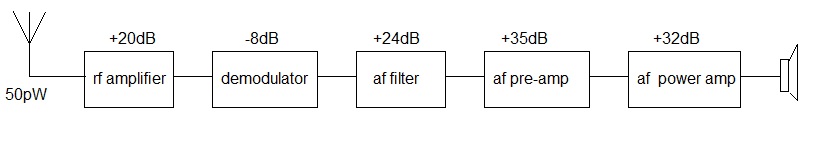
=> for an input of 50pW, the power output would be ~1W.
Power is more difficult to measure than voltage, and since P = V2/R, a voltage form is often used.
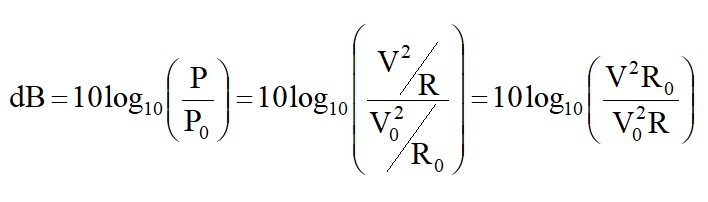
Unfortunately, this expression is often used incorrectly when R ≠ R0, though in many cases, the error introduced is small.