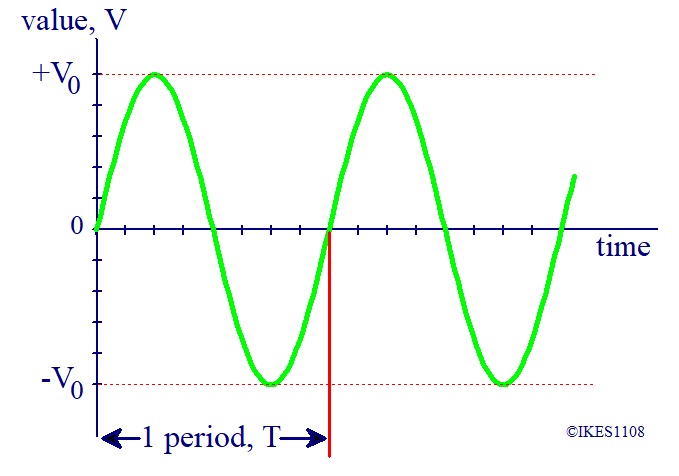
Basic Sine Wave
Sine function.
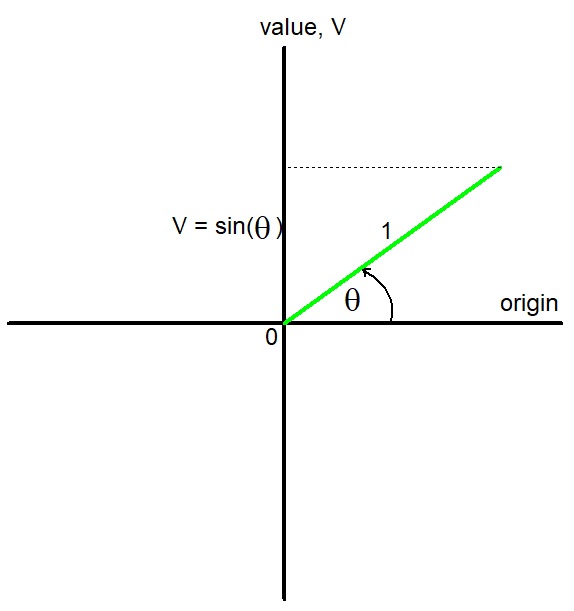
The projection of the green line onto the value axis has a length V = sin(θ).
Now consider the green line rotating at a constant angular speed, ω, about 0, as in the diagram below.
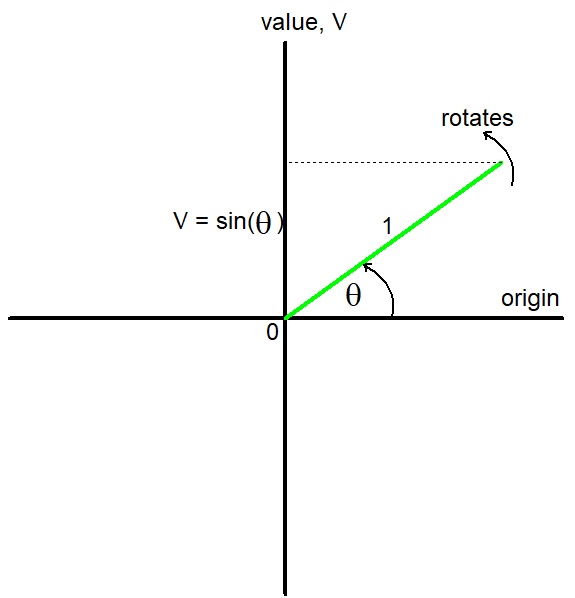
so => V = sin(ωt)
If the green line does one complete revolution in time T (time period), then 2π = ωT andso => V = sin(2πt/T)
But frequency, f, is equal to 1/T, so ω = 2πfso => V = sin(2πft)
or the equation could be left as V = sin(ωt), where ω is the 'angular frequency' = 2πfTo make the value of V larger than 1, the length of the green line is multiplied by a constant, V0
=> V = V0sin(ωt) or V = V0sin(2πft)
A graph of V against time is shown below.